Everything you want to know about the point of access for a domestic's electricity, from an electric panel breakdown to a way to hook solar panels into your own home's power gadget.
Churning with voltage and akin to an explosion at the twine manufacturing unit, the breaker panel exudes mystique. But it's only a big transfer, filled with other smaller switches, which cause the switches that any domesticproprietor can fearlessly turn. Doing so conjures a cutting-edge of electrons that runs along copper wires, energizing our home equipment, lighting fixtures and cutting-edge lives. Breaker-panel literacy isn't only for voltage veterans who recite the National Electrical Code. Even if all you surprise is whether or not your humble warm bathtub desires are electrically potential, or why the toaster oven kills the kitchen lighting—the panel has a element or to inform you.
NEUTRAL AND HOT WIRES
Current flows from the panel toward the load alongside the hot wires and returns alongside the neutral. Each hot cord's copper tip ultimately connects to its manage switch on the circuit breaker, and every neutral connects to a commonplace terminal referred to as a bus bar.
BREAKER SIZES
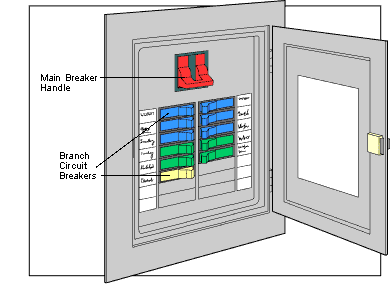
Main breaker
This is the on/off transfer to the complete breaker panel. A two hundred-amp breaker is suitable for a home upwards of 2000 square feet. Smaller buildings can use a hundred and fifty-amp or a hundred-amp; small houses and sub panels can use as low as 50-amp.
Double-pole breaker
Uses the entire 240 volts available to the panel. The 15-amp and 20-amp breakers frequently take care of baseboard warmers, 30-amp serve water heaters and electric dryers, 40- and 50-amp are for electric powered ranges, and the 70-amp ought to serve a massive air conditioner or a sub panel.
Single-pole breaker
The 15-amp and 20-amp are all-purpose breakers, strolling the entirety from lighting and retailers to storage-door openers.
15-amp AFI breaker
Arc-fault-circuit-interrupter breakers can prevent fires resulting from accidental electric discharge.
WIRE GAUGE
12-gauge cord
Common for low-demand connections to light switches and stores, attached to either 15- or 20-amp breakers.
14-gauge cord
Too skinny for something aside from 15-amp breakers under small loads.
10-gauge cord
Appropriate for a -pole 20-amp breaker or a single-pole 30-amp breaker.
8-gauge or 6-gauge twine
Used for forty-, 50- and 60-amp two-pole breakers; big appliances. Also used to serve sub panels.
GROUND WIRES
Grounding prevents a conductor now not meant to hold cutting-edge (such as the steel side of a clothes dryer) from causing injury if it's energized by a frayed hot wire. In a well grounded gadget, appliances and steel containers join lower back to the grounding bus of the breaker panel. From there, the device is grounded to the earth via buried ground rods.
HOW ELECTROCUTION HAPPENS
Ventricular traumatic inflammation, the erratic, deadly spasm that takes place as electric powered cutting-edge passes via the heart, occurs whilst both of a person's arms touch hot and impartial conductors, causing the contemporary to finish its circuit thru the chest. In a floor fault, modern can circulate a unmarried hand, zapping the heart because it passes thru the body on its way to the ground. When changing live fuses within the antique days, electricians labored with one hand whilst keeping the alternative in their again pocket--this spared the heart by isolating the present day to the nerves of the one hand within the fuse field.
What Is the Watt?
Found in electric reference books everywhere, the Ohm's regulation wheel simplifies conversions among watts, volts, ohms and amps. The maximum vital calculation for a purchaser is voltage instances amperage, which equals wattage—an appliance's energy requirements—and the basis of the unit in which energy is offered.
Juice Routes
As home-brewed electricity gets more sophisticated, expect to look gadgets now bought as separate hardware—inclusive of sun panel inverters and AC/DC disconnects, or generator subpanels and switch switches—merge into single, general elements, which are easier to install and understand
Installing a Backup Generator: In a energy outage, a backup generator presents electricity to designated circuit breakers. Natural gas or propane fuels the generator's engine, which spins an alternator to create a magnetic field that sends contemporary to the home. It's crucial that no energy from the generator returned-feeds to the grid—linesmen running to repair energy could be electrocuted. An automated switch transfer isolates the generator's power to keep it off the grid till power is restored. Then the generator shuts down and the transfer switch reverses.
Wiring Wind Turbines or Solar Photovoltaics: Solar panels and wind mills feed DC power into an inverted, which converts it to AC for home use. AC and DC disconnect switches permit elements to be remote for service. These structures continuously again-feed to the grid, however in the course of a blackout—to a few grid-tied clients' surprise—their electricity can't be used. One solution: Store electricity in a battery backup gadget. Inverts like Outback Power's Flex power One reduce device charges with prewired battery connections and circuit breakers. New micro-inverts convert DC to AC at the panel, eliminating DC wiring runs.
The Smart Grid in Your Basement
Some advantages purchasers ought to see upon crowning glory of a country wide smart grid are already to be had in products like Computerized Electric Systems' Smart Panel. Computer hardware hacked onto a popular breaker panel allows this tool to display character circuits, transfer and stability loads among energy sources, or control energy remotely. Simply having extra statistics about each breaker's power consumption can be the start of a more electrically green lifestyle—depart the fridge's door open, witness the actual-time intake spike, and get encouraged.
















0 comments:
Post a Comment